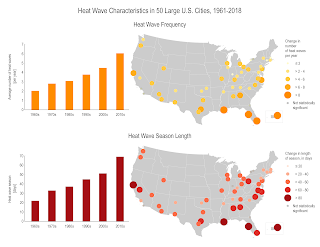
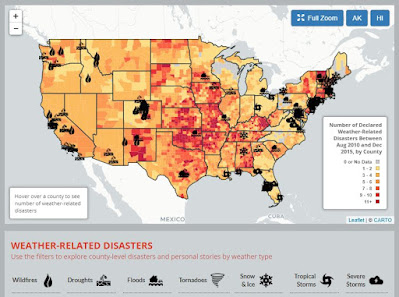
When I think about coastal erosion, I think about Pacifica, CA, and the 2016 after el Niño related storms, when yet another chunk of sandy cliff was falling into the ocean and houses were in need of abandonment. A drone video of the area is clear. A lot of information can be found about how in a few years the cliff has eroded.
Recently two online portals have been developed as an interactive tool for any user to explore what coastal hazards are all about:
The NOAA’s Sea Level Rise Viewer website let you browse over possible scenarios of sea level rise and coast vulnerability. A great link to try!
Today I am going to focus on another link, the USGS Coastal Change Portal. The USGS Coastal Change Hazards Portal is a new tool that allows anyone to explore how coasts change due to: extreme storms, shoreline change, and sea level rise.
Extreme Storms: this allows ‘real-time and scenario-based predictions of storm-induced coastal change, as well as the supporting data, are provided to support management of coastal infrastructure, resources, and safety.’ For example, let’s focus on the Gulf Coast and a scenario of a hurricane (any category). Let’s see how a Cat 1 and a Cat 5 possibly looks like (with probabilities of collision (dune erosion), overwash, and inundation for sandy beaches along the Gulf and Atlantic coasts during a generalized hurricane landfall): see figures for both. The most probable areas should be risks areas and treated as such in an emergency.

Shoreline Change: this shows: ‘historical shoreline positions and rates of change along ocean shorelines of the United States’. Looking into the East coast now, offshore Norfolk, see figures for long-term coastal change rates, and for the short-term rates (<30 years rates of shoreline change for open-ocean shorelines of the United States ranging from 1970's to 2001).
Sea level Rise: there are two methods used to address this: a Coastal Vulnerability Index (CVI), and a probabilistic assessment of shoreline change.
CVI: ‘a preliminary overview, at a National scale, of the relative susceptibility of the Nation's coast to sea-level rise through the use of CVI. This classification is based upon the following variables: geomorphology, regional coastal slope, tide range, wave height, relative sea-level rise and shoreline erosion and accretion rates. The combination of these variables and the association of these variables to each other furnish a broad overview of regions where physical changes are likely to occur due to sea-level rise’. A quick image shown here shows how much red (very high vulnerability) our California coasts possess.
 Probabilities of Shoreline Change: ‘this dataset was used to develop and evaluate the performance of a Bayesian network (BN) that predicts long-term shoreline change associated with sea-level rise. The BN is used to define relationships between driving forces, geologic constraints, and coastal response, which includes observations of local rates of relative sea-level rise, wave height, tide range, geomorphology, coastal slope, and rate of shoreline change. Using this information, the BN is used to make probabilistic predictions of shoreline change in response to different future sea-level rise scenarios’.
Probabilities of Shoreline Change: ‘this dataset was used to develop and evaluate the performance of a Bayesian network (BN) that predicts long-term shoreline change associated with sea-level rise. The BN is used to define relationships between driving forces, geologic constraints, and coastal response, which includes observations of local rates of relative sea-level rise, wave height, tide range, geomorphology, coastal slope, and rate of shoreline change. Using this information, the BN is used to make probabilistic predictions of shoreline change in response to different future sea-level rise scenarios’. As you can see this new tool will help tremendously to manage areas and to get a broad idea of what is happening on the US coasts.
Explore those links!-
 Probabilities of Shoreline Change: ‘this dataset was used to develop and evaluate the performance of a Bayesian network (BN) that predicts long-term shoreline change associated with sea-level rise. The BN is used to define relationships between driving forces, geologic constraints, and coastal response, which includes observations of local rates of relative sea-level rise, wave height, tide range, geomorphology, coastal slope, and rate of shoreline change. Using this information, the BN is used to make probabilistic predictions of shoreline change in response to different future sea-level rise scenarios’.
Probabilities of Shoreline Change: ‘this dataset was used to develop and evaluate the performance of a Bayesian network (BN) that predicts long-term shoreline change associated with sea-level rise. The BN is used to define relationships between driving forces, geologic constraints, and coastal response, which includes observations of local rates of relative sea-level rise, wave height, tide range, geomorphology, coastal slope, and rate of shoreline change. Using this information, the BN is used to make probabilistic predictions of shoreline change in response to different future sea-level rise scenarios’.